Keywords
algae
EC50
ecotoxicology
effective concentration
feature importance
infrared spectroscopy
machine learning.
Abstract
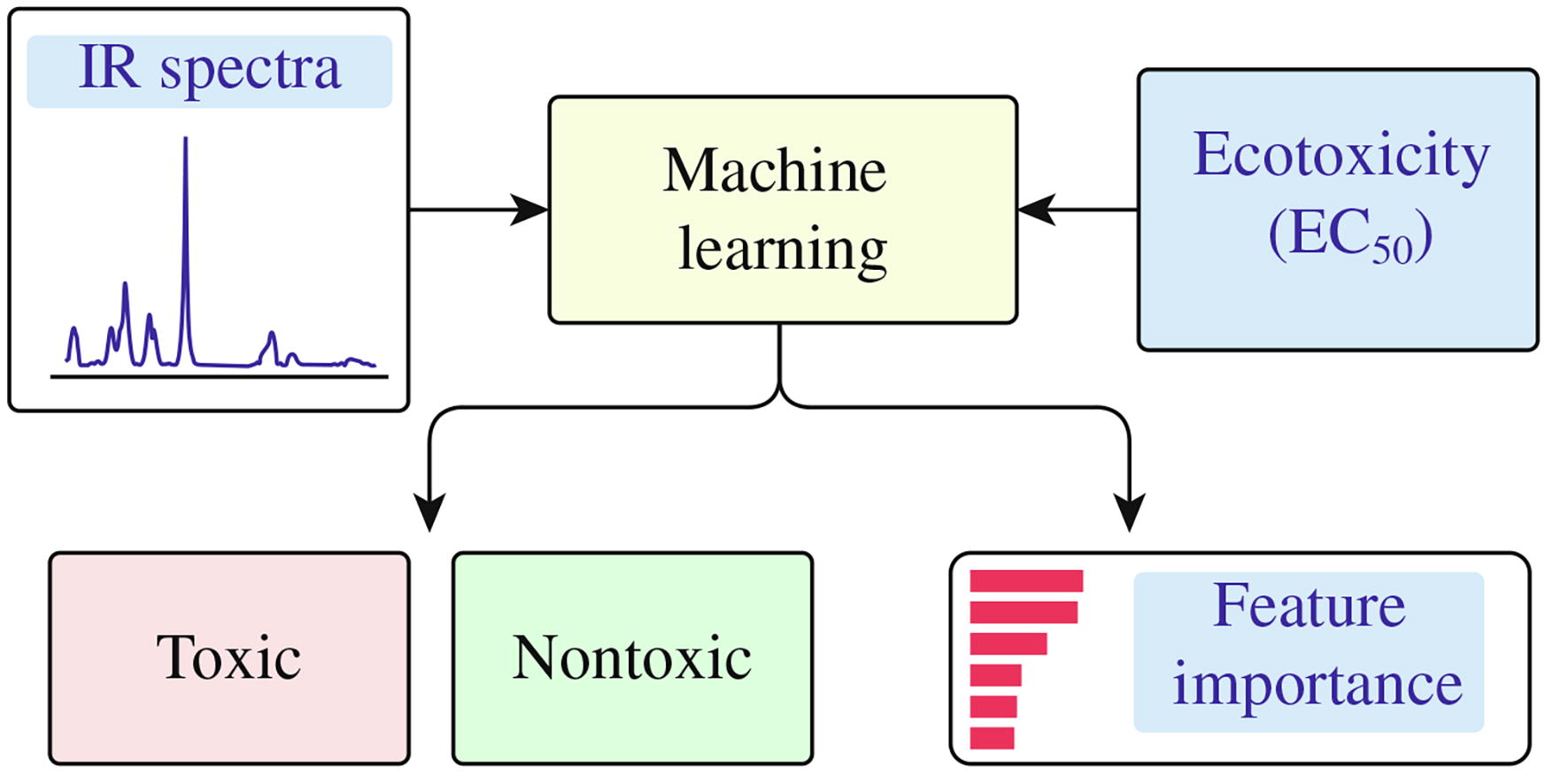
A new, less time-consuming and resource-intensive approach to predicting the EC50 ecotoxicity index, which is crucial for assessing the impact of compounds on ecosystems, is proposed. Efficient EC50 prediction based on infrared spectroscopy data and EC50 values from the EcoTOX database is achieved using machine learning. The best results with an F1-score of 0.83 were obtained with the SVC and XGBoost models.
References
.

Bondarenko L., Illés E., Tombácz E., Dzhardimalieva G., Golubeva N., Tushavina O., Adachi Y., Kydralieva K.
Nanomaterials,
2021
.

Carvalho D.V., Pereira E.M., Cardoso J.S.
Electronics (Switzerland),
2019
.

Vo A.H., Van Vleet T.R., Gupta R.R., Liguori M.J., Rao M.S.
Chemical Research in Toxicology,
2019
.

Olker J.H., Elonen C.M., Pilli A., Anderson A., Kinziger B., Erickson S., Skopinski M., Pomplun A., LaLone C.A., Russom C.L., Hoff D.
Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry,
2022
.

Pukalchik M.A., Katrutsa A.M., Shadrin D., Terekhova V.A., Oseledets I.V.
Journal of Soils and Sediments,
2019
.

Cunningham P., Delany S.J.
ACM Computing Surveys,
2021
.
Bondarenko L., Saveliev Y., Chernyaev D., Baimuratova R., Dzhardimalieva G.I., Dzeranov A., Kelbysheva E., Kydralieva K.
Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,
2023
.

Schür C., Gasser L., Perez-Cruz F., Schirmer K., Baity-Jesi M.
Scientific data,
2023
.

Koshelev D.S.
Applied Spectroscopy,
2024