Keywords
Abstract
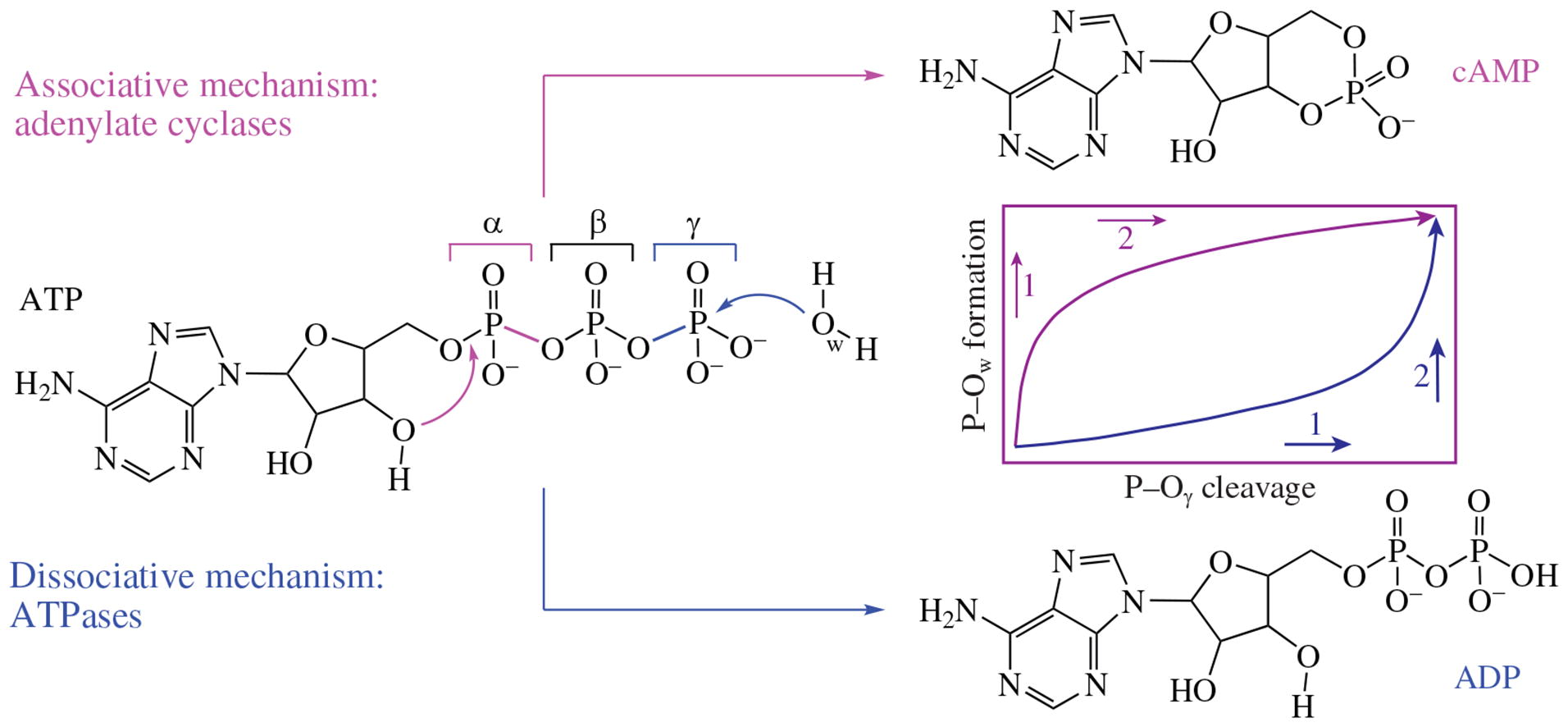
Recent achievements in molecular modeling of reaction mechanisms of the enzymatic ATP conversion to ADP or cAMP are discussed. Both of these reactions are initiated by the nucleophilic attack of an oxygen atom, but the P–O bridging bond cleavage occurs via different mechanisms, dissociative and associative. These mechanisms differ in the order of formation and cleavage of P–O bonds. For ATP ases, the dissociative mechanism is assumed, whereas ATP conversion to the cAMP occurs via associative mechanism. We suggest a novel approach based on the molecular dynamics simulations with combined quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics potentials of the enzyme–substrate complexes that can discriminate dissociative and associative reaction pathways by analysis of length distributions of the cleaving and forming P–O bonds.
References