Keywords
cation-exchangeresincontent
demineralization
electroconvection
electrodialysis
flicker noise spectroscopy.
heterogeneousmembrane
laser interferometry
phenylalanine
water splitting
Abstract
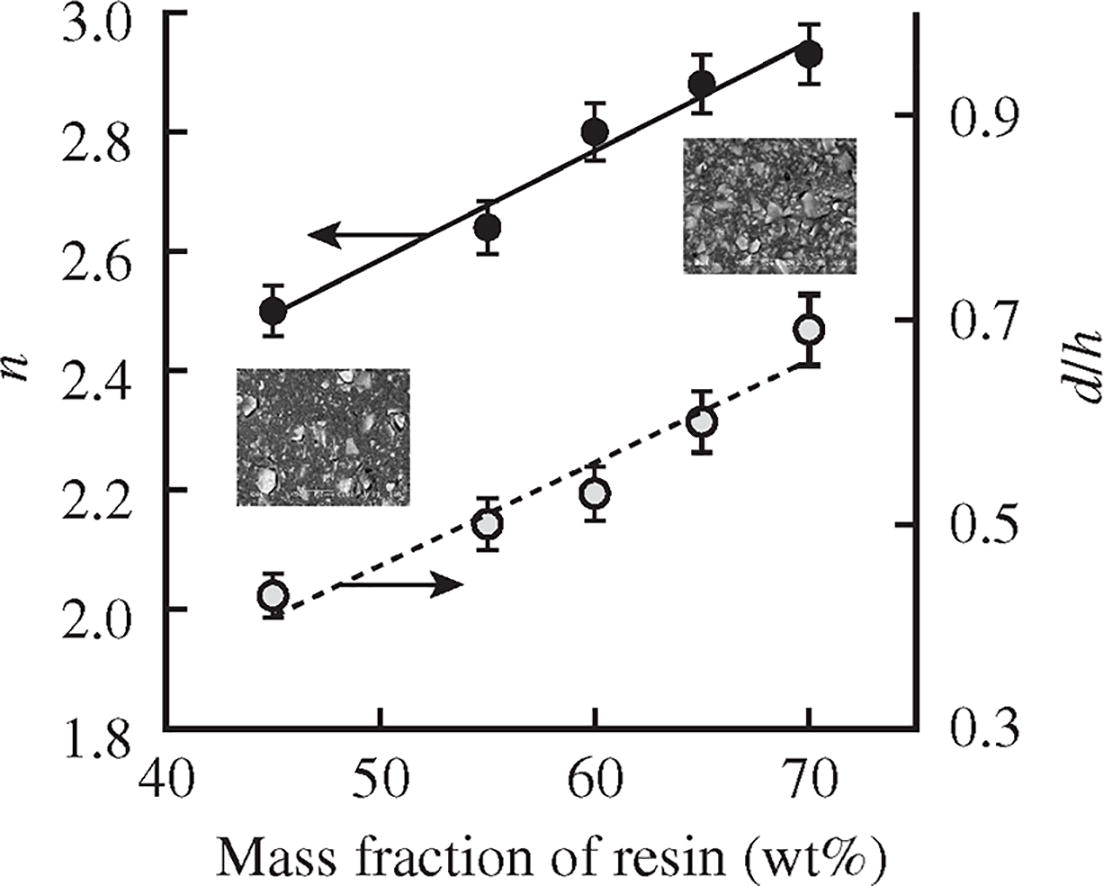
For the first time, direct evidence was obtained using laser interferometry and flicker-noise spectroscopy that the main cause of the increase in the transport of amino acids through a sulfonated cation-exchange membrane in intense current modes is electroconvection. The turbulent nature of electroconvective vortices at the solution/membrane interface, acidification of the solution in the demineralization compartment and a substantial intensification of amino acid fluxes under over-limiting current modes were revealed. This indicates the electroconvective destruction of the barrier effect of the solution layer with a high pH value near the cation-exchange membrane.
References
.
Yaroslavtsev A.B., Stenina I.A.
Mendeleev Communications,
2021
.

Lin X., Pan J., Zhou M., Xu Y., Lin J., Shen J., Gao C., Van der Bruggen B.
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,
2016
.

TIMASHEV S.F., POLYAKOV Y.S.
Fluctuation and Noise Letters,
2007
.

Akberova E.M., Vasil'eva V.I.
Electrochemistry Communications,
2020
.

Zyryanova S., Mareev S., Gil V., Korzhova E., Pismenskaya N., Sarapulova V., Rybalkina O., Boyko E., Larchet C., Dammak L., Nikonenko V.
International Journal of Molecular Sciences,
2020
.
Vasil’eva V.I., Akberova E.M., Zabolotsky V.I., Novak L., Kostylev D.V.
Petroleum Chemistry,
2018
.

Vyas P.V., Ray P., Adhikary S.K., Shah B.G., Rangarajan R.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,
2003
.

Simons R.
Electrochimica Acta,
1985
.

Shaposhnik V.A., Eliseeva T.V.
Journal of Membrane Science,
1999
.

Eliseeva T., Kharina A.
Membranes,
2022
.

Eliseeva T.V., Shaposhnik V.A.
Russian Journal of Electrochemistry,
2000
.

Grib H., Belhocine D., Lounici H., Pauss A., Mameri N.
Journal of Applied Electrochemistry,
2000
.

Choi J., Oh S., Moon S.
Journal of Chemical Technology and Biotechnology,
2002
.

Belova E., Lopatkova G., Pismenskaya N., Nikonenko V., Larchet C.
Desalination,
2006
.

Vasil'eva V., Zabolotsky V., Shaposhnik V., Zhiltsova A., Grigorchuk O.
Desalination and Water Treatment,
2010
.

Sun Z., Gao X., Zhang Y., Gao C.
Desalination and Water Treatment,
2016
.

Wenten I.G., Khoiruddin K., Alkhadra M.A., Tian H., Bazant M.Z.
Advances in Colloid and Interface Science,
2020
.

Liu L., Yang L., Jin K., Xu D., Gao C.
Separation and Purification Technology,
2009
.

Aghajanyan A.E., Hambardzumyan A.A., Vardanyan A.A., Saghiyan A.S.
Desalination,
2008
.

Elisseeva T.V., Shaposhnik V.A., Luschik I.G.
Desalination,
2002